WARP FPGA Board Power Supplies
Required External Supply
The WARP FPGA board operates from a single external 12v supply. This supply is generally connected to the board's coaxial power connector. This connector requires a mating female connector with an inner diameter of 2.1mm, outer diameter of 5.5mm, positive tip and grounded shell. We use a 50W AC-DC regulator from CUI (ETS120416UTC-P5P-SZ), available from Digikey (part T1010-P5P-ND).
FPGA Power Supplies
The Virtex-4 FPGA has a number of different power inputs. The table below summarizes the power supplies on the WARP FPGA board.
| Supply | Voltage | Description |
| VCC_EXT | 12v | External supply |
| VCC_5 | 5.0v | Daughtercard slot supply |
| VCC_INT | 1.2v | FPGA core logic |
| VCC_AUX | 2.5v | FPGA clock resources |
| VCC_O | 3.3v, 2.5v & 1.8v | FPGA I/O banks |
| MGT_x | 2.5v, 1.5v & 1.2v | MGT logic and I/O |
| VCC_0.9 | 0.9v | DDR2 SO-DIMM termination |
The WARP FPGA board uses switching voltage regulators for the 5v, 3.3v, 1.8v and 1.2v supplies. All are are Texas Instruments' PTH12020W 18A DC-DC power modules.
The 2.5v VCC_AUX supply is a LT1764 linear regulator from Linear Technology.
The MGT supplies are all driven by linear supplies in order to minimize noise in the MGT circuitry. Three linear regulators (2 LT1963A and 1 LT1764) are used.
Daughtercard Power Supplies
The four daughtercard slots on the WARP FPGA board are supplied with 5v by a dedicated 18A switching regulator. A second power plane is also connected to the daughtercard slots and can be driven by an off-board supply via a dedicated 6-pin header on the FPGA board (J31). This header is not mounted by default (no current WARP daughtercards utilize this second plane).
Monitoring Voltage Levels
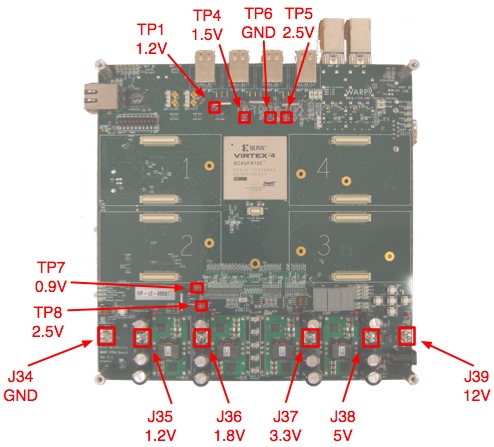
Every power and ground plane on the FPGA board includes a test point or screw terminal which can be used to monitor the plane's voltage. There are also test points and a screw terminal for ground. The locations of the test points and screw terminals are illustrated in the figure below.
Most supplies (12v, 5v, 3.3v, digital 2.5v and MGT 2.5v) include a red LED which glows when power is applied. These five LEDs should always be illuminated when the FPGA board is powered on. If any of these LEDs is not glowing, immediately power off the board to avoid damaging components.
Bypassing Power Supplies
The WARP FPGA board does not contain any built-in current measurement capabilities. In order to measure current consumption, the power plane of interest can be driven by an external, off-board supply whose current can be measured. When an external supply is used, the on-board regulator for the plane must be disabled to avoid a drive fight between the on-board and off-board supplies. Eight of the FPGA board's supplies (5v, 3.3v, 2.5v, 1.8v, 1.2v, MGT 2.5, MGT 1.5 and MGT 1.2v) can be individually disabled. To disable these regulators, simply mount a shunt on the jumper adjascent to the regulator; see the table below for the specific reference designators for each jumper.
High-current screw terminals are connected to the primary power planes: GND, 12v, 5v, 3.3v, 1.8v and 1.2v and can be used to connect external supplies. See the image below to identify the screw terminals.
Primary Supplies
| Plane | Regulator | Disable Jumper | Screw Terminal | Test Point |
| 12v | Ext | - | J35 | TP14 |
| 5v | U18 | J32 | J38 | TP12 |
| 3.3v | U16 | J33 | J37 | TP11 |
| 2.5v | U8 | J40 | - | TP8 |
| 1.8v | U13 | J42 | J36 | TP10 |
| 1.2v | U11 | J43 | J35 | TP13 |
| GND | - | - | J34 | TP9 |
MGT Supplies
| Plane | Regulator | Disable Jumper | Test Point |
| 2.5v | J3 | J8 | TP5 |
| 1.5v | U2 | J7 | TP4 |
| 1.2v | U1 | J9 | TP1 |